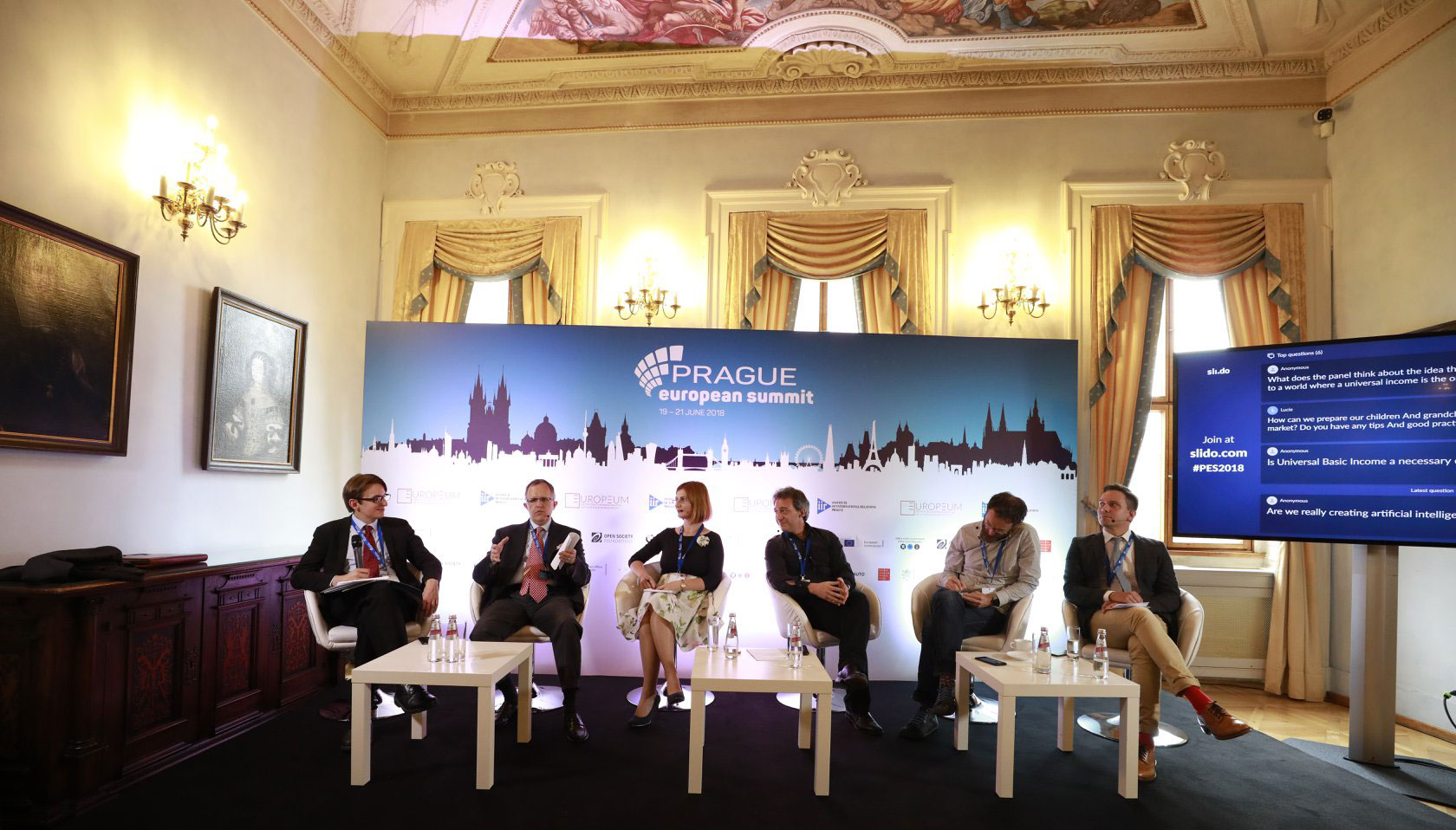
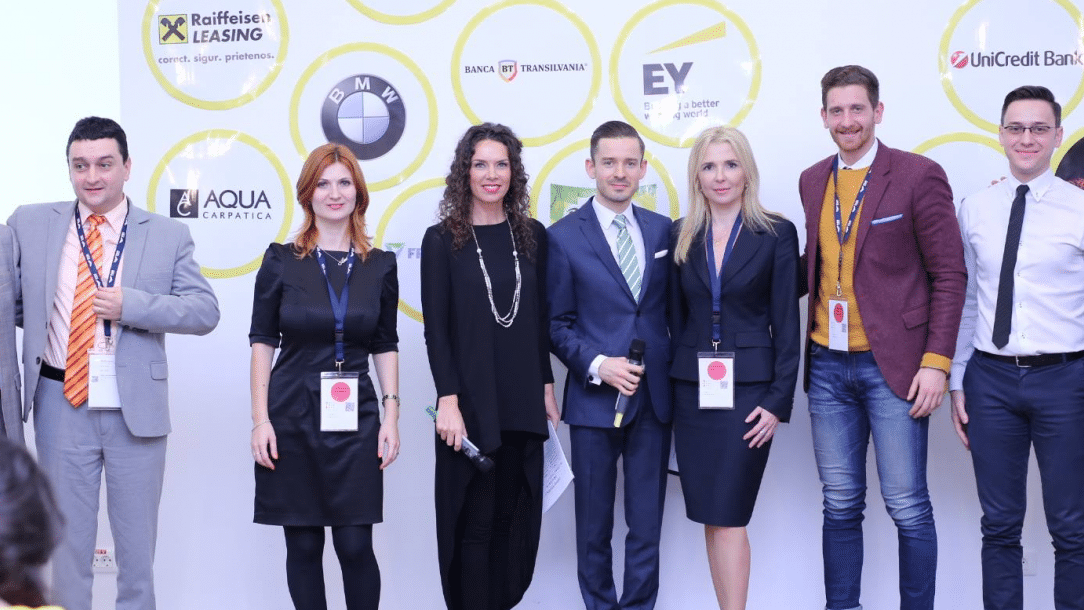
On June 19, 2018, MKOR Consulting attended the Prague European Summit to discuss with industry specialists the impact that robotization, digitalization, and automation have on the labor market.
Thus, Corina Cimpoca — the founder of MKOR Consulting — was part of the panel Automation, Robotization, and Transformation of the Labour Market: Impacts for Central Europe.
The discussion between representatives of European think tanks, academia, and the business environment sought to answer a series of questions regarding the future of the labor market in the context of Industry 4.0.
How affected will it be by new technologies? Which industries will undergo changes? How can we respond to these changes?
MKOR Consulting’s contribution to the debate consisted of data and insights from the Romanian business landscape, aimed at anchoring the discussion in the reality of the business environment.
What is Industry 4.0?
Industry or Industrialization 4.0 is the computerized transformation of manufacturing and other industries. Computerization consists of connecting robotic machines to the internet, systematizing services, and using vast amounts of information to make work more efficient.
Industry 4.0 involves the digitalization, automation, and/or robotization of work processes, based on new technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), algorithms, the Internet of Things (IoT), Big Data, etc.
The Origin of Industry 4.0
The term Industry 4.0 was adopted in 2011 by an initiative group consisting of representatives from various industries (business, politics, and education) with the aim of improving competitiveness in the manufacturing industry.
The idea was adopted by the German federal government in the High-Tech Strategy for 2020.
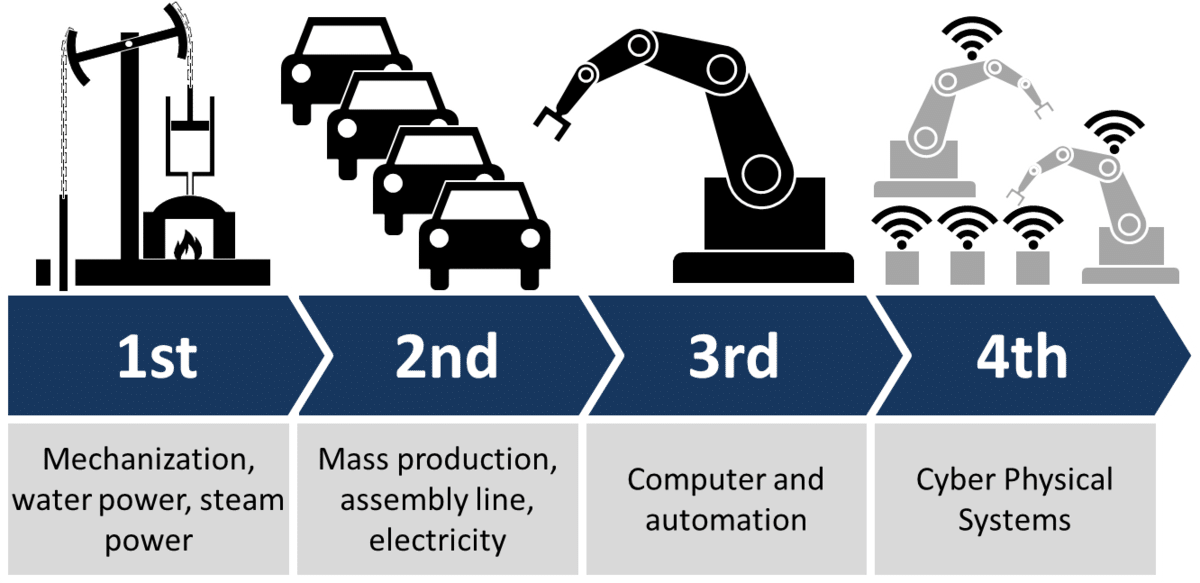
History of Industry 4.0
- The First Industrial Revolution took place in Great Britain in the 18th century when production was supported by steam engines.
- The Second Industrial Revolution (1870 – 1914) was defined by the invention of the telegraph and railroads, which led to better connectivity. Factory electrification contributed to mass production.
- The Third Industrial Revolution (1950 – 1970) came with the shift from analog to digital systems. It is also known as the Information Age, during which computers and technological communications were developed.
In the Fourth Industrial Revolution, factories will become autonomous and self-monitoring; machines will communicate with each other and with humans and will have the capacity to make decisions.
In such a scenario, what will happen to employees? Will Europe be affected? Is Romania ready to respond to new technologies? MKOR specialists sought to answer these questions through a study.
How will automation impact employees?
According to a recent study conducted by MKOR, in which over 150 business leaders from Romania across a wide range of industries were surveyed, the expected impact is positive (90% of respondents).
Romanian business leaders maintain that the impact of digitalization, automation, and robotization will be visible in terms of improved productivity and efficiency, shorter delivery times, fewer human errors, and tasks being completed more easily.
Of course, cost reduction is an impact felt through the reduction of expenses in the human resources department.
Automation is an opportunity, business leaders believe
In addition, leaders see the automation of certain tasks as an opportunity for them and their employees to develop new skills and focus on more strategic tasks, such as innovation or business development.
Regarding the impact on jobs, some leaders believe they will decrease, but at the same time, this represents an opportunity for those employees directly affected by automation to develop new skills, reduce repetitive tasks, raise the standards of final results, and reduce human effort and costs.
For the most part, automated processes take over basic intellectual tasks (e.g., data entry) and technological processes (e.g., programming). Thus, employees freed from these tasks have the opportunity to develop new skills to focus on work that demands the intellect more intensely.
Internet of Things (IoT), robotic machines, and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are the most common solutions for the robotization and automation of work processes in Romanian companies.
Furthermore, 85% of leaders believe that the automation of work processes in their companies will provide new competitive advantages.
How can we restructure the economy to face new challenges?
To face the new challenges brought by the digitalization of work processes, digital education and the way society manages to provide an environment conducive to the development of digital skills are important.
The formal educational system
According to the International Computer and Information Literacy Study (ICILS), which evaluates the level of digital skills of 8th-grade students from 21 educational systems worldwide, 17% of them do not even reach the basic level of the evaluation scale, while only 2% obtain the maximum score.
Furthermore, 25% of students in 7 out of 9 EU countries do not have digital skills. In this context, it is important to recognize these problems and seek their resolution.
How can we ensure that internet access is equal for our children and that no one will be left behind?
Continuous training
Is it necessary for adults to acquire new skills and abilities to remain competitive in the labor market? Are companies willing to offer them training programs in this regard?
Our study respondents have already identified the impact that automation will have on their companies: 95% have already started redistributing work tasks, 82% have started continuous learning programs for all employees, and retraining affected employees (70%).
Adapting to change
Many jobs will not be replaced by robots but will undergo changes. Adapting to change is the solution that can bring added value in the context of jobs threatened by change.
The solution lies in the hands of all actors, public and private, who with a proactive attitude should find solutions to take advantage of technological opportunities rather than viewing them as threats.
Which industrial sectors will benefit?
According to the preliminary results of the study developed by MKOR, most companies have started the automation and robotization of work processes.
These companies come from IT & C, financial services, management & consulting, and energy. It is also expected that manufacturing, construction, and agriculture will be impacted.
More than half of the interviewed companies have started the automation process, most frequently in the IT department (71%), Operations and Production (67%), and in the Finance department (62%).
Stay up to date with MKOR initiatives
We constantly develop our own research on challenging topics and are always up to date with the news. If you want to keep up with business changes, subscribe to the newsletter!
You will receive specialized articles, white papers, and you will have a say on the most burning topics.
Have you read everything? Comment / join our newsletter / read our other research posts!
Micro-moments in the Digital Era. MKOR at Business Days Cluj 2016
January 25, 2026
0 Comments16 Minutes